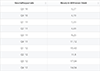
Pertussis, also known as whooping cough, is on the rise worldwide. Data from the World Health Organization (WHO) shows that 941,101 cases were reported last year, up from 163,388 diagnoses in 2023 - an increase of 476 percent. As the following chart shows, cases of diphtheria, tetanus and rubella have also ticked up in recent years. The WHO warns that the increases seen right now are partly due to declining vaccination coverage, as even small declines can “dramatically raise the risk of disease outbreaks and place additional strain on already overstretched health systems.”
Vaccine coverage can drop for various reasons, including whether a region has limited access to immunization services, if there has been a disruption to supply or if people believe misinformation about vaccines. Conflict and instability can also hinder vaccine access by disrupting healthcare systems, as well as resulting in disrupted infrastructure and the displacement of populations.